In order to implement the requirements of relevant documents such as the Outline of the "Healthy China 2030" Plan, the "Healthy China Action (2019-2030)", the Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on Promoting the High Quality Development of Public Hospitals, and promote the construction of smart hospitals and hospital information standardization in the "three in one" of electronic medical records, smart services, and smart management, conform to the new business trends such as Internet diagnosis and treatment, smart medical consortia, and explore the use of new technologies such as intelligence to improve medical quality and efficiency. On May 28, 2024, the Hospital Management Research Institute of the National Health Commission held an academic exchange conference in Beijing on the theme of "integrating intelligence, strengthening quality, and assisting development" to promote the high-quality development of public hospitals through smart hospitals.

The revision process of the new standard took one year, from 2023 to 2024. Starting from April 1, 2023, the revision of the grading evaluation standards for electronic medical records will be initiated. From April 2 to 8, 2023, based on extensive solicitation of suggestions from hospitals and industry experts, as well as a summary and analysis of common audit issues over the years, 26 standard revision meetings will be held.
From the perspective of the conference venue, a comparative analysis of hospital informationization investment in 2022 and 2023 has been conducted, as follows (data from PPT materials at the conference venue):
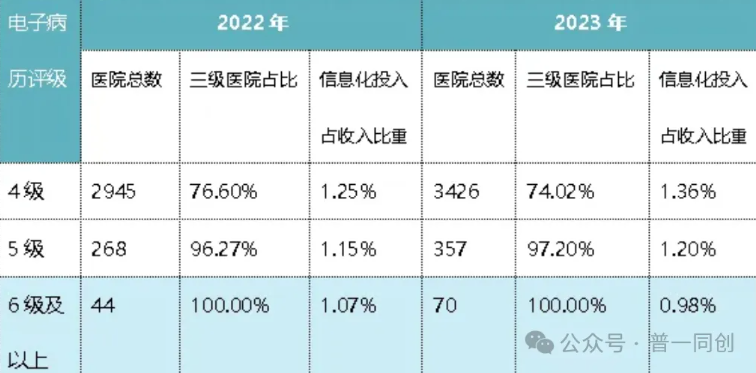
In 2023, the average number of hospital information departments in China was 7.68, with an average of 69.28 beds per information worker; The average number of information departments in secondary hospitals is 4.17, with an average of 71.68 beds per information worker; The average number of information department personnel in tertiary hospitals is 14.71, with an average of 68.4 beds per information personnel.
The new standard has redesigned the indicator architecture, including the removal of some low-level transitions; Cancel duplicate work and improve the practicality of standards; Language should be unified, rigorous, and free from doubt; The total number of indicators has decreased from 779 to 754; Data quality sampling, no need to prepare all SQL, reducing workload by about 50-70%; Increased the degree of freedom in selection, reducing the minimum number of entries from 70% of the total to around 50%.
The level is set to levels 1-8, and level 0 is no longer retained. The specific levels are as follows:

The evaluation content and roles have been adjusted, some have been deleted, some have been added, some have been adjusted, and some have been deleted. Firstly, 2 new roles were added and their names were adjusted, bringing the total number of roles to 12; Next, 8 new projects were added, 6 were merged and reduced, 3 were deleted, and the total number of projects was adjusted to 38. Specifically, as follows:
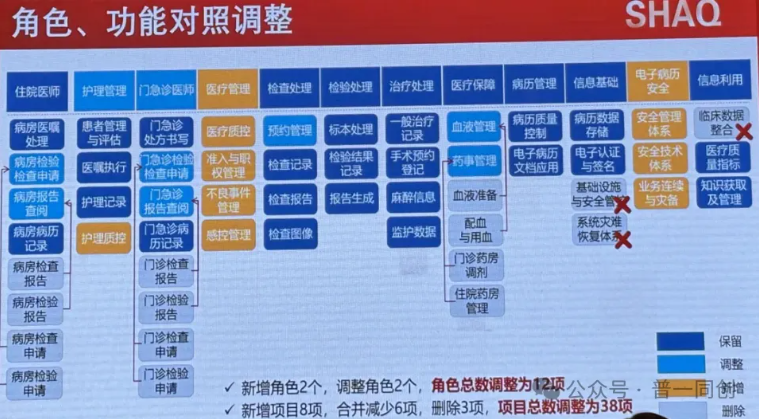
Two additional roles have been added, including medical management and electronic medical record security. Medical management requirements include medical quality control, nursing quality control, access and authority management, adverse event management, and infection control management. Strengthen security management, refine security responsibilities at different levels, enhance "human defense" in the security management system, strengthen "physical defense" and "technical defense" in the security technology system, enhance business continuity and disaster recovery, and require strengthened operation and maintenance support to ensure business operation.

After adjustment, a total of 752 new evaluation indicators were added, 282 were added, 253 were adjusted, 220 were retained, and 308 were deleted (including 198 merged). Among them, there are 22 items at level 1, 46 items at level 2, 79 items at level 3, 106 items at level 4, 151 items at level 5, 156 items at level 6, 106 items at level 7, and 75 items at level 8.
In addition, the role of electronic medical record security has been added, forming a collaborative protection between information infrastructure and electronic medical record security. The necessity of electronic medical record security is explained from four dimensions: national industry requirements, international security landscape, and medical informationization, business, and security.
The new standard has merged the functions. Highlighting the key points, including merging (outpatient, inpatient) inspection and testing applications into (outpatient, inpatient) inspection and testing applications, merging (outpatient, inpatient) inspection and testing reports into (outpatient, inpatient) report review, merging blood preparation, matching, and use into blood management, and merging outpatient drug dispensing and ward drug configuration into pharmaceutical management.
The new standard refers to the requirements of the "Interpretation of the Key Points of the 2023 Medical Quality and Safety Core System" and the "Comprehensive Improvement of Medical Quality Action (2023-2025)", and adds 68 new requirements, accounting for 9.0%. For example, it includes drug classification management for physicians and nurses, self medication management, consultation, external examination, critical value, adverse events, hospital acquired infections, and so on; Graded and classified management for surgical management, new technology management, surgical verification, surgical transportation, etc; Special blood type management, special blood use management, and blood use process management for blood use; Internet medical record management and medical record archiving management for medical record management.
The new standard has put forward requirements for regional collaboration. According to the overall national policy requirements, the use of regional data is required starting from level 5, involving 55 items, accounting for 7%. Starting from level 5, emphasis is placed on querying regional data, while levels 6 and 7 both emphasize the utilization of regional data. Level 8 emphasizes the health and self collection management of regional data.
The new standard further improves closed-loop management and specifies requirements for 22 closed-loop scenarios. The unified sentence structure is: support Closed loop management enables real-time monitoring of The status of each stage, including. Specifically, it includes the closed loop of medical orders, examination records, inspection process, drug use, consultation, adverse events, and treatment process.
The new standard has added requirements for traditional Chinese medicine and herbal medicine, and added 32 evaluation items. Mainly including traditional Chinese medicine: classification, decoction machine reading labels, decoction related requirements; Knowledge base: Examination of the eighteen taboos, nineteen fears, and contraindications in traditional Chinese medicine; TCM treatment: TCM clinical pathway, acupuncture and moxibustion, acupoints and other requirements; Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) medical records: structured content such as TCM disease diagnosis, TCM syndrome diagnosis, and four diagnostic information; Format and writing standards for traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions; Nursing records: records of nursing interventions.
The new standard adds a requirement for "artificial intelligence". This includes artificial intelligence applications such as scheme recommendation, auxiliary judgment, medical record generation, quality control of medical record content, as well as digital therapies such as post hospital diagnosis and treatment plans and self collected data to form treatment plans. Among them, "smart voice dialogue" will be adjusted to the new version of the "Smart Services" standard.
The new standard adds requirements for "medical integration" and "clinical nutrition". Starting from level 7 of smart healthcare, 10 new evaluation criteria will be added, including support for exercise prescription issuance by ward physicians and outpatient physicians, prescription sharing, multi-party collaborative support, and exercise prescription library; General treatment records include exercise prescriptions, intervention management, wearable device access, databases, and medication management for food allergies, knowledge bases, nutritional adjustments, etc.
The new standard has adjusted the integration description. If it can be uniformly managed and adjusted in the hospital, it can be integrated and displayed uniformly in the hospital; The unified management mechanism of the entire hospital has been adjusted to an integrated management mechanism.
The new standard has added a requirement for "localization substitution". Considering the trend of innovation, OFD and innovation requirements have been added, totaling 7 items, accounting for 0.9%. OFD has good support for mixed storage of text and images, with additional Beidou requirements for time sources and the use of national encryption algorithms for encryption.
The new standard adds a requirement for "usability". Add 35 usability requirements to the implementation method, including three aspects: direct on-screen display, color labeling, and real-time prompts.
The new standard redefines the levels corresponding to key requirements. Considering the rapid development of informatization, some high-level functions will be moved down. Intermediate logic check, including examination conditions such as name, diagnosis, age, etc., all adjusted to level 5; The importance of security requirements has been downgraded from level 5-6 to level 3-4, with basic requirements for fire protection and other security measures added, as well as requirements for personal information protection and data security.
The evaluation dimension has been adjusted from the original 4 dimensions to 5 dimensions, including uniqueness, completeness, compliance, identity, and timeliness. Uniqueness mainly tests whether the key record identification is unique, to prevent operational errors caused by duplicate records, and to prevent patients from making false claims; Integrity mainly tests whether the fields are complete, whether the recorded content is complete, whether the system design is compliant, and whether the data records are sufficient to support medical quality management; Compliance (unified dictionary, data logic, time logic) mainly examines whether there is a unified dictionary for the entire hospital, whether the data storage format is correct, whether the logical relationship is correct, whether the internal logic of the system is reasonable, whether the unified dictionary and format ensure the normal operation of the system, and whether the data storage logic is reasonable, such as time; Identity mainly tests whether the definitions of fields with the same name are the same, whether project objects can be compared, and the degree of data integration between systems to avoid confusion in data definitions; Timeliness mainly tests whether data synchronization is timely, whether the data synchronization time between systems is smooth, and whether the process is smooth.
The new standard has designed the evaluation approach using a scoring calculation method. Fully consider the business characteristics of each medical institution, do not emphasize the requirement for "basic items", evaluate all content, and give initial scores according to the examination items, divided into 5 points, 3 points, and 1 point. 5 points are for key functions, system core functions, or key requirements for medical quality management projects, 3 points are for recommended functions, encouraging construction or technology trend projects, and 1 point is for optional functions, selecting construction projects. Firstly, evaluate whether the corresponding level has been passed according to the roles, accumulate the scores for each role, and if the score is greater than 80% of the total score, it is considered passed.
The new standard has revised the functional evaluation. In previous evaluations, it was found that important indicators could not be counted and the application of inspection services hindered the improvement of medical quality. Therefore, data quality and effective application were considered as "single veto items" in the evaluation.
Source | Reprinted by the National Health Commission Source: Zhiyixin
Disclaimer: The articles marked as the source on this WeChat are all reposts and are only for sharing purposes. If there are any copyright issues, please contact us as soon as possible, and we will correct or delete them as soon as possible. Thank you




