Smart service rating and related processes
In March 2019, the National Health Commission issued the "Hospital Smart Service Grading Evaluation Standard System (Trial)" document, making hospital smart service rating one of the new smart hospital rating requirements after the release of electronic medical record rating requirements.
In 2021, the first batch of 29 hospitals in China were evaluated and passed the Level 3 review (including 1 Level 4 and others all Level 3).
The objectives, objects, grading, methods, evaluation items and specific requirements of the evaluation related to smart service rating have been clearly stated in the document "Hospital Smart Service Grading Evaluation Standard System (Trial)". If necessary, you can download the relevant documents or refer to the previous article "Problems to Know in Hospital Smart Service Grading Evaluation" on your personal official account.
Regarding the application process, you can refer to the requirements of the "Notice of the National Health Commission and the Medical Administration Bureau on Carrying out the 2021 Hospital Smart Service Grading Evaluation and Smart Management Self evaluation Work", which will not be elaborated here.
Issues and challenges of intelligent service informatization
Due to the recent development of smart service rating, most hospitals are still unfamiliar with it. Therefore, the biggest challenge for hospitals at present is how to carry out the information technology work involved in the rating, and how to implement the specific requirements for hospital smart service grading evaluation in the smart service rating document.
There will be two issues encountered here: firstly, there are many systems involved in the rating of smart services. The following figure is a personal summary of the systems that may be involved in smart services (levels 1-5):
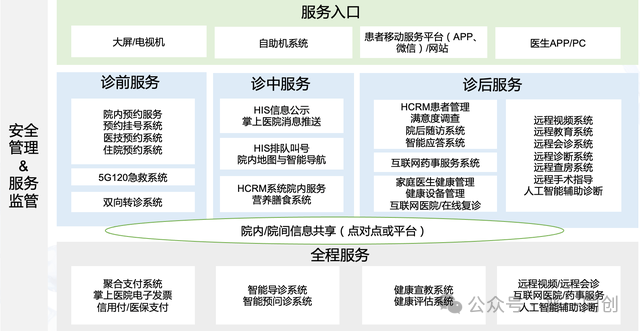
Another issue is the matching between rating requirements and the system.
Smart service rating is a requirement for results and does not explicitly specify the system and method of implementation. Therefore, when comparing functions, it is necessary to determine how to implement and in which system to implement it.
Due to the lack of clear specification of the implementation system in the rating requirements, it is unclear which system the specific functions should be implemented in, and the key points cannot be grasped. Especially for systems that were not originally built in hospitals, it is unclear how to improve them. If the implementation path and method are taken incorrectly, it may result in double the workload.
Smart Service Level 3 8 Major Systems
How can we focus on the key points and efficiently carry out smart service rating work in response to the previous issues? The key here is to grasp several core systems of smart service rating.
Although there are many systems involved in the overall evaluation of smart services, most hospitals already have some basic systems, such as self-service machines, in-hospital queuing and calling, and room appointments; The difference is generally not significant, and some may not require much modification or can be modified slightly.
Based on our construction experience, most hospitals currently lack or have significant gaps in the following eight systems for the Level 3 requirement of smart service rating. These eight systems are critical to the current situation, and with the modifications mentioned above, we have basically grasped the backbone and can achieve "eight or nine without ten". On the contrary, without the support of these systems, it is very difficult to rectify and lacks a lever.
The specific 8 systems are as follows:
1. Appointment diagnosis and treatment system
The first part of the rating requirements for "pre consultation services" is "appointment for diagnosis and treatment", which is the core requirement for appointment services for visits, examinations, and treatments.
Some appointment services and diagnosis functions within the hospital are generally available in HIS systems, with minor modifications needed for those that are not.
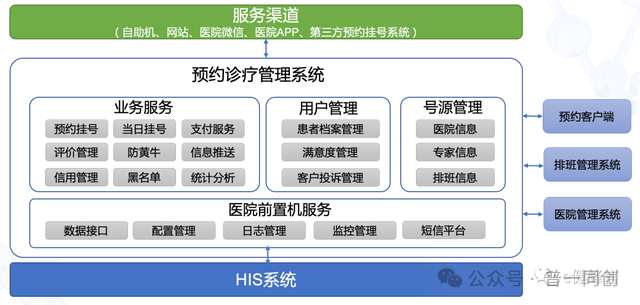
The most required content here is related to appointment registration, including: information exchange between patients inside and outside the hospital, support for multiple ways of appointment registration, notification of changes in hospital information, sharing of internal and external number sources, appointment scheduling at different times, direct medical treatment in appointment rooms, blacklist management, and so on. And these are all basic items.
One implementation mode here can be processed through HIS+handheld hospital appointment registration module, while the other can consider establishing a separate appointment diagnosis and treatment management system to achieve overall management of business, user, and number source scheduling, as shown in the figure below. The specific method can be selected based on the actual situation of the hospital.
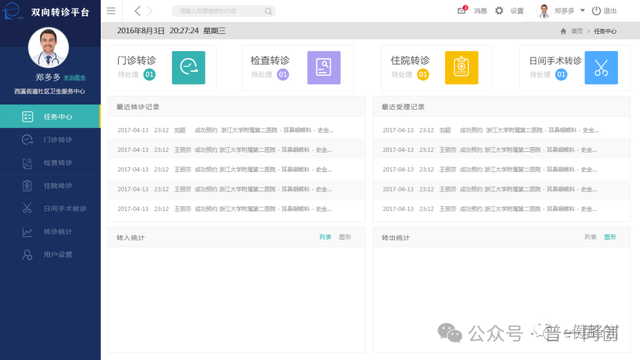
2. Two way referral system
The "referral service" is the third part of the "pre consultation service" requirements, which mainly include: being able to receive referrals, supporting the input of external information and achieving intra hospital sharing, supporting the acquisition of external information and storing it in the hospital information system, etc.
In addition, there are higher requirements for levels four and five. Due to the construction of medical consortia and medical communities, referral services are basic requirements. It is best to establish a two-way referral system that not only meets the rating requirements, but also helps the construction of medical consortia and medical communities.
3. Handheld hospital system
Palm hospital (APP or WeChat official account, applet), as the main tool of patient service, is the most important content of intelligent service. In the rating requirements, whether it is "pre consultation service", "in consultation service", "post consultation service" or "full-service", as the entrance to the service, there are relevant requirements.
From the perspective of the functions of the handheld hospital system, although currently all hospitals have basically established their own official account, service numbers, and small programs, and most have also achieved the functions of pre payment check, there are still many gaps in the specific requirements of smart service rating, which need to be improved and modified.
Regarding mobile hospitals, there are some requirements for Level 3 hospitals, please refer to the rating document for details:
(1) The "diagnosis and treatment appointment" function of "pre diagnosis service" requires support for various diagnosis and treatment appointment service requirements mentioned in the previous appointment diagnosis and treatment system.
(2) The requirements for "in clinic services" include multiple functions, including proactive push of various medical information; Notification of diagnosis and treatment activities; The functional module includes real-time query services, such as appointment registration and payment processing status; Notification of various diagnosis and treatment activities; Notification of inspection precautions, medication guidance, and other information; There are also identification and navigation functions; And patient convenience guarantee services, etc.
(3) The requirements for "post diagnosis services" include patient feedback, patient management, medication dispensing and distribution, family services, and guidance from primary physicians. The vast majority of the content requires interaction through mobile devices.
(4) Finally, the "full-service" section requires payment of fees, intelligent medical guidance, health education, and other content to be implemented in a mobile hospital as the service entrance requires mobile devices.
Overall, mobile devices are important job responsibilities, and specific modifications and additions can be made according to relevant requirements.
Just some functions can be directly implemented on the mobile end in combination with the HIS system, such as the "information push", "identification and navigation", and "patient convenience guarantee service" required by the three-level review for "in patient services"; The "drug dispensing and distribution" of "post diagnosis services"; The implementation of "full service", "intelligent medical guidance", "health education", etc. can be considered in this way.
And some other functions require support from backend systems, such as many of the systems mentioned in this article.
4. Patient satisfaction survey system
The first part of "post diagnosis service" is "patient feedback", which focuses on the investigation of patient satisfaction. Correspondingly, it is a patient satisfaction survey system that requires the ability to provide feedback through various devices (self-service machines, mobile phones), covering different diagnosis and treatment stages, actively pushing, supporting complaints, and one click feedback functions.
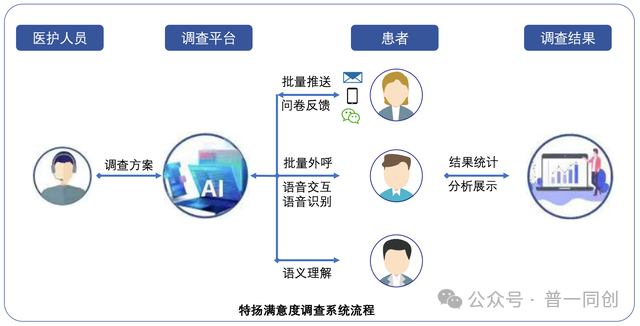
5. Post hospital follow-up management system
The "Patient Management" section of the "After Diagnosis Services" corresponds to the HCRM system with health management functions. The requirements for the third level rating mainly include: follow-up and personalized reminder services, among which the follow-up requirements include the ability to develop personalized follow-up plan content, communication between the follow-up system and HIS information, and support for multiple follow-up methods.
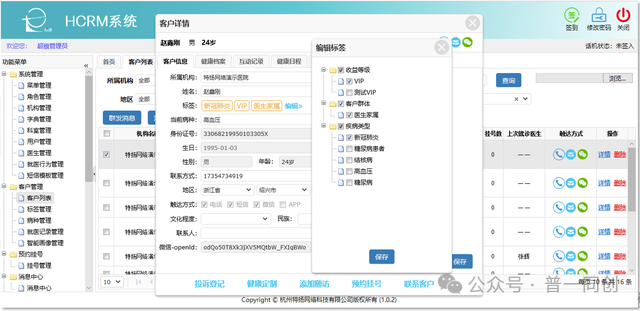
6. Family Medical Contract Service System
The "family services" of "post diagnosis services" mainly correspond to the management of home doctor contract services, including the use of information systems for contract management, support for online appointment of home medical care or services, and online remote follow-up visits by family doctors.
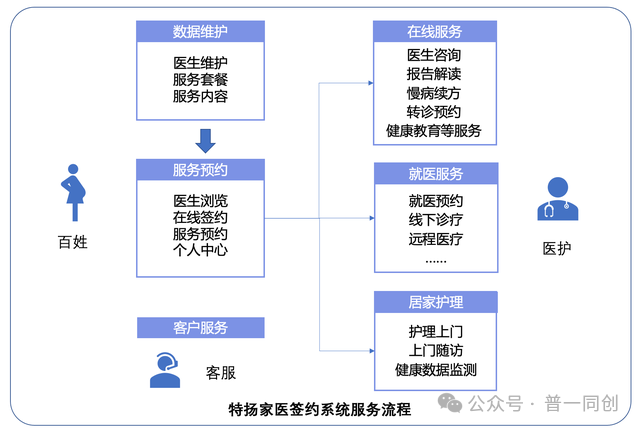
If the online remote re diagnosis here is to be realized, it must be connected to the Internet hospital system. However, this requirement is optional and its proportion is not high, so hospitals can choose according to the actual situation. In addition, door-to-door service also involves online nursing system, which is similar to Internet hospitals.
7. Remote medical system
The "grassroots physician guidance" in "post diagnosis services" and the "telemedicine" in "full-service" correspond to telemedicine related systems, including remote consultation, remote imaging, remote electrocardiogram, remote laboratory and other functions. One of the requirements for the three-level evaluation of remote imaging, remote electrocardiogram, and remote laboratory can be achieved.
Remote consultation has many requirements in full-service telemedicine, such as real-time interactive consultation, simultaneous display of diagnosis and treatment materials and videos, support for mobile devices for consultation, etc. Therefore, remote consultation is basically a must-have system.
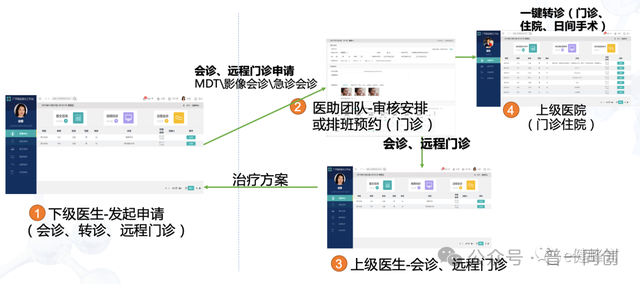
Remote imaging, remote electrocardiography, and remote laboratory are currently widely used, and one can choose according to the actual situation of the hospital. If the hospital does not need them, these are not mandatory options. If the score is sufficient, it is also possible not to build them.
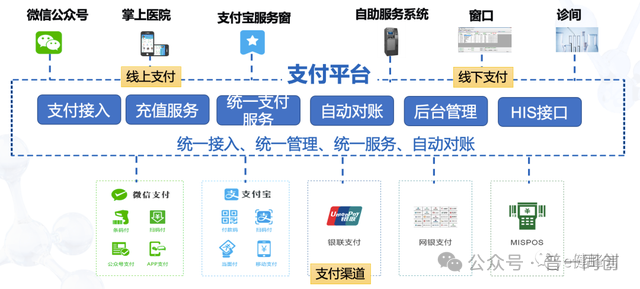
8. Unified Payment System
The "fee payment" entrance of "full-service" includes windows, consultation rooms, self-service machines, mobile terminals, etc. The supporting system corresponds to an aggregated payment platform system.
Due to the fact that mobile payment is basically a necessary item for people to seek medical treatment, and now the payment methods are diversified without system support, the workload of financial reconciliation is very large, so this system is also one of the required systems.
In addition to the eight major systems mentioned above, there is also the "emergency connection" of "pre diagnosis service", which is not a mandatory option in the third level rating and does not require high requirements. Therefore, it is possible to consider improving the existing emergency system of the hospital. In addition, the "security management" in "Basic and Security" mainly involves infrastructure, which can be improved according to corresponding comparisons. The final 'service supervision' mainly refers to the content of data reporting, which can generally be compared and modified.
Afterword
Due to the aforementioned issues, there are still many confusions in the construction of smart services, especially in terms of the systems that need to be built. The above is aimed at the content listed in the third level of smart services. By grasping the eight core key systems mentioned above, we can grasp the backbone of the evaluation and greatly improve efficiency.
Of course, the Level 3 review also involves other non critical systems, which may not have high requirements or are not mandatory. Specific hospitals can choose to implement them according to their actual situation.
In addition, if it is level 4 or 5, there will be more systems involved, but currently it is not possible to bypass the level rating, only to level by level rating. So in the actual construction process, hospitals with conditions can also plan or partially implement higher-level systems according to the actual needs of the hospital, such as medical technology appointment systems, pre hospital emergency systems, in-hospital dynamic navigation, artificial intelligence, and other related systems. Each hospital can also arrange according to its actual situation.


